Install shell script execution platform
- Choose the running platform
For Windows, there are 3 options:
- Command Prompt (cmd)
- Or, Windows Subsystem for Linux (WSL)* on Windows 10: https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/wsl/install-win10
- Or, WSL2* on Windows 10: https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/wsl/wsl2-install
*choose Ubuntu 18.04 LTS distro either way
For Linux, there are 2 options:
- Ubuntu 18.04.4 LTS (Bionic Beaver): https://releases.ubuntu.com/18.04.4/
- Or, Ubuntu 20.04 LTS (Focal Fossa): https://releases.ubuntu.com/20.04/
Instructions for Command Prompt on Windows:
- Change directory to home in command prompt
cd %HOMEDRIVE%%HOMEPATH%
- Install Git in command prompt
- Install Git for Windows: https://git-scm.com/download/win
Note - if you freshly installed git for windows then you need to close and start a new command prompt to refresh path environment variable.
- Clean kthw-azure-git directory, if already exists
rd %HOMEDRIVE%%HOMEPATH%\kthw-azure-git /S
- Clone git repo into kthw-azure git directory
git clone https://github.com/ankursoni/kubernetes-the-hard-way-on-azure.git %HOMEDRIVE%%HOMEPATH%\kthw-azure-git
- Install docker in command prompt:
- Install Docker for Windows: https://docs.docker.com/docker-for-windows/install
- Build docker image with the image name as kthw-azure-image
cd %HOMEDRIVE%%HOMEPATH%\kthw-azure-git\infra
docker build -t kthw-azure-image .
- Run docker container in interactive terminal with kthw-azure-git directory mounted from the host machine
docker run -it --name=kthw-azure-container --mount type=bind,source=%HOMEDRIVE%%HOMEPATH%\kthw-azure-git,target=/root/kthw-azure-git kthw-azure-image bash
# if the above command fails with the error 'Unhandled exception: Drive has not been shared' then you need to share your windows home drive (most likely c:) with docker inside docker Settings > Resources > File Sharing
https://stackoverflow.com/questions/59942110/docker-drive-has-not-been-shared
# to logout from container
exit
- Resume the docker container in interactive terminal
# start the containeras it may be in stopped state because of logout
docker start kthw-azure-container
# attach to the current running process - bash in the started container
docker attach kthw-azure-container
Note - here onwards for next instructions and commands, always run inside docker container using the steps mentioned above
All done with prerequisites on command prompt, now head to section - Provision infrastructure on cloud
Instructions for Ubuntu, WSL or WSL2 users:
- Change directory to home in bash terminal
cd ~
- Update and upgrade apt packages:
{
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get full-upgrade -y
}
- Install basic prereuisites:
sudo apt-get install -y \
apt-transport-https \
ca-certificates \
curl wget unzip tar openssl git \
lsb-release \
gnupg-agent gnupg2 \
software-properties-common
- Clean kthw-azure-git directory, if already exists
rm ~/kthw-azure-git -rf
- Clone git repo into kthw-azure git directory
git clone https://github.com/ankursoni/kubernetes-the-hard-way-on-azure.git ~/kthw-azure-git
Install remaining pre-requisites as docker image (recommended)
- Install docker ce on WSL:
- Install Docker for Windows: https://docs.docker.com/docker-for-windows/install
- Enable docker integration in WSL:
a. https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/virtualization/community/team-blog/2017/20171208-wsl-interoperability-with-docker
b. Or, https://nickjanetakis.com/blog/setting-up-docker-for-windows-and-wsl-to-work-flawlessly
- Install docker ce on WSL2:
- Install Docker for Windows: https://docs.docker.com/docker-for-windows/install
- Enable docker integration in WSL2: https://code.visualstudio.com/blogs/2020/03/02/docker-in-wsl2
- Install docker ce on Ubuntu 18.04:
{
curl -fsSL "https://download.docker.com/linux/$(lsb_release -is | tr -td '\n' | tr [:upper:] [:lower:])/gpg" | sudo apt-key add -
echo "deb [arch=amd64] https://download.docker.com/linux/$(lsb_release -is | tr -td '\n' | tr [:upper:] [:lower:]) \
$(lsb_release -cs | tr -td '\n' | tr [:upper:] [:lower:]) stable" | sudo tee -a /etc/apt/sources.list.d/docker.list
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get install -y docker-ce docker-ce-cli containerd.io
}
- Install docker on Ubuntu 20.04:
sudo apt-get install docker-compose
- Build docker image with the image name as kthw-azure-image
cd ~/kthw-azure-git/infra
docker build -t kthw-azure-image .
- Run docker container in interactive terminal with kthw-azure-git directory mounted from the host machine
docker run -it --name=kthw-azure-container --mount type=bind,source=$HOME/kthw-azure-git,target=/root/kthw-azure-git kthw-azure-image bash
# to logout from container
exit
- Resume the docker container in interactive terminal
# start the containeras it may be in stopped state because of logout
docker start kthw-azure-container
# attach to the current running process - bash in the started container
docker attach kthw-azure-container
Note - here onwards for next instructions and commands, always run inside docker container using the steps mentioned above
All done with prerequisites for docker image, now head to section - Provision infrastructure on cloud
Or, install remaining pre-requisites directly on Linux or WSL host (not recommended)
- Change directory to home
cd ~
- Install az cli
# if this fails on latest Ubuntu 20.04, refer to https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/cli/azure/install-azure-cli-apt?view=azure-cli-latest#manual-install-instructions and replace $AZ_REPO with 'bionic'
curl -sL https://aka.ms/InstallAzureCLIDeb | sudo bash
- Install kubectl
{
curl -s https://packages.cloud.google.com/apt/doc/apt-key.gpg | sudo apt-key add -
echo "deb https://apt.kubernetes.io/ kubernetes-xenial main" | sudo tee -a /etc/apt/sources.list.d/kubernetes.list
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get install -y kubectl
}
- Install terraform
{
wget https://releases.hashicorp.com/terraform/0.12.24/terraform_0.12.24_linux_amd64.zip
unzip terraform_0.12.24_linux_amd64.zip
sudo mv terraform /usr/local/bin/
rm terraform_0.12.24_linux_amd64.zip
}
- Verify terraform installation
terraform -v
Provision infrastructure on cloud
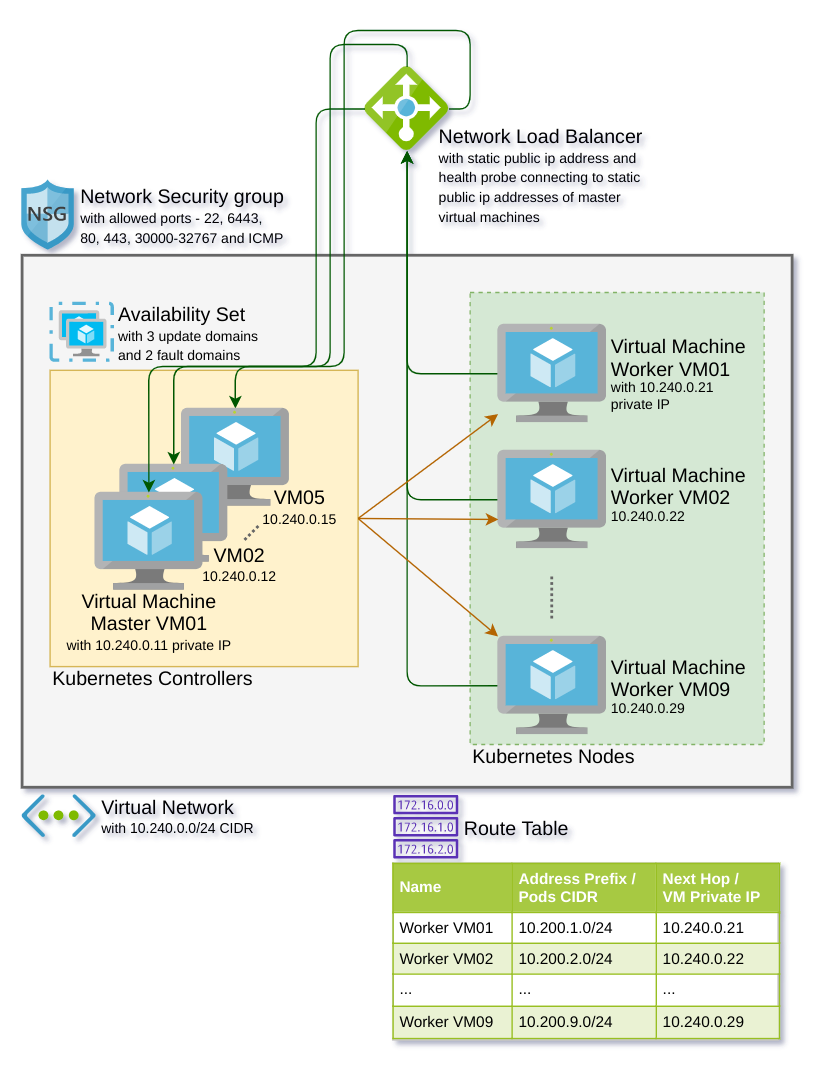
- Set the values for the variables by writing to the var file - azurerm-secret.tfvars
cd ~
az login
az account list
# note the id as <SUBSCRIPTION_ID> and tenantId as <TENANT_ID> from the output of previous command
# generate an azure service principal with contributor permissions, if you don't already have one:
az ad sp create-for-rbac --role="Contributor" --scopes="/subscriptions/<SUBSCRIPTION_ID>"
# note the appId as <CLIENT_ID> and password as <CLIENT_SECRET> from the output of previous command
# generate an ssh key, if you don't already have one:
ssh-keygen -b 4096 -t rsa -C <EMAIL_ADDRESS>
# note the path of the file "~/.ssh/id_rsa.pub" as <SSH_PUBLIC_KEY_FILE>
# to make system remember the private key passphrase:
exec ssh-agent bash
ssh-add
# copy the template variable file
cd ~/kthw-azure-git/infra
cp azurerm.tfvars azurerm-secret.tfvars
# subscription, tenant, service principal and ssh variables
# substitute the value for <SUBSCRIPTION_ID> by replacing PLACEHOLDER in the following command:
sed -i 's|<SUBSCRIPTION_ID>|PLACEHOLDER|g' azurerm-secret.tfvars
# for e.g., the command to substitute the value for <SUBSCRIPTION_ID> with 794a7d2a-565a-4ebd-8dd9-0439763e6b55 as PLACEHOLDER looks like this:
sed -i 's|<SUBSCRIPTION_ID>|794a7d2a-565a-4ebd-8dd9-0439763e6b55|g' azurerm-secret.tfvars
# substitute the value for <TENANT_ID> by replacing PLACEHOLDER in the following command:
sed -i 's|<TENANT_ID>|PLACEHOLDER|g' azurerm-secret.tfvars
# substitute the value for <CLIENT_ID> by replacing PLACEHOLDER in the following command:
sed -i 's|<CLIENT_ID>|PLACEHOLDER|g' azurerm-secret.tfvars
# substitute the value for <CLIENT_SECRET> by replacing PLACEHOLDER in the command
sed -i 's|<CLIENT_SECRET>|PLACEHOLDER|g' azurerm-secret.tfvars
# substitute the value for <SSH_PUBLIC_KEY_FILE> by replacing PLACEHOLDER in the command
# PLACEHOLDER e.g. "~/.ssh/id_rsa.pub"
sed -i 's|<SSH_PUBLIC_KEY_FILE>|PLACEHOLDER|g' azurerm-secret.tfvars
# prefix, environment and location variables
# these 3 variables help in naming the azure resources
# for e.g., resource group name: <PREFIX>-<ENVIRONMENT>-rg01
# for e.g., master virtual machine name: <PREFIX>-<ENVIRONMENT>-mastervm01.<LOCATION_CODE>.cloudapp.azure.com
# for e.g., worker virtual machine name: <PREFIX>-<ENVIRONMENT>-workervm01.<LOCATION_CODE>.cloudapp.azure.com
# for e.g., network load balancer name: <PREFIX>-<ENVIRONMENT>-apiserver.<LOCATION_CODE>.cloudapp.azure.com
# substitute the value for <PREFIX> by replacing PLACEHOLDER in the following command:
# PLACEHOLDER e.g. "kthw" or "kube" etc.
sed -i 's|<PREFIX>|PLACEHOLDER|g' azurerm-secret.tfvars
# substitute the value for <ENVIRONMENT> by replacing PLACEHOLDER in the command
# PLACEHOLDER e.g. "demo" or "play" or "poc" or "dev" or "test" etc.
sed -i 's|<ENVIRONMENT>|PLACEHOLDER|g' azurerm-secret.tfvars
# substitute the value for <LOCATION> by replacing PLACEHOLDER in the command
# PLACEHOLDER e.g. "Australia East" or "Southeast Asia" or "Central US" or "West Europe" etc.
# run this to know more: "az account list-locations -o table"
sed -i 's|<LOCATION>|PLACEHOLDER|g' azurerm-secret.tfvars
# master variables
# substitute the value for <MASTER_VM_SIZE> by replacing PLACEHOLDER in the command
# PLACEHOLDER e.g. "Standard_B1ms" or "Standard_DS2_v2" etc. with ssd disk capabilities indicated by 's'
# run this to know more: "az vm list-sizes --location "<LOCATION>" -o table"
sed -i 's|<MASTER_VM_SIZE>|PLACEHOLDER|g' azurerm-secret.tfvars
# substitute the value for <MASTER_VM_COUNT> by replacing PLACEHOLDER in the command
# PLACEHOLDER e.g. 1 or 2 etc. upto a maximum of 5
# choose 1 if you are learning and later auto-scale
sed -i 's|<MASTER_VM_COUNT>|PLACEHOLDER|g' azurerm-secret.tfvars
# worker variables
# substitute the value for <WORKER_VM_SIZE> by replacing PLACEHOLDER in the command
# PLACEHOLDER e.g. "Standard_B1ms" or "Standard_DS2_v2" etc. with ssd disk capabilities indicated by 's'
# run this to know more: "az vm list-sizes --location "<LOCATION>" -o table"
sed -i 's|<WORKER_VM_SIZE>|PLACEHOLDER|g' azurerm-secret.tfvars
# substitute the value for <WORKER_VM_COUNT> by replacing PLACEHOLDER in the command
# PLACEHOLDER e.g. 1 or 2 etc. upto a maximum of 9
# choose 1 if you are learning and later auto-scale
sed -i 's|<WORKER_VM_COUNT>|PLACEHOLDER|g' azurerm-secret.tfvars
# verify the auzurerm-secret.tfvars file by displaying its content
cat azurerm-secret.tfvars
# output should be something like this
subscription_id="794a7d2a-565a-4ebd-8dd9-0439763e6b55"
tenant_id="<removed as secret>"
client_id="<removed as secret>"
client_secret="<removed as secret>"
prefix="kthw"
environment="demo"
location="Australia East"
ssh_public_key_file="~/.ssh/id_rsa.pub"
master_vm_size="Standard_B1ms"
master_vm_count=1
master_disk_size_gb=32
worker_vm_size="Standard_B1ms"
worker_vm_count=1
worker_disk_size_gb=32
enable_health_probe=false
enable_master_setup=false
enable_worker_setup=false
# if there is a correction needed then use text editor 'nano' to update the file and then press ctrl+x after you are done editing
nano azurerm-secret.tfvars
- Deploy infrastructure
cd ~/kthw-azure-git/infra
# initialise terraform providers
terraform init
# execute infrastructure provisioning command
terraform apply -var-file=azurerm-secret.tfvars
# if terraform throws any error, it may be due to dns name conflicts with already deployed infrastructure in the chosen azure location.
# try to workaround these errors by changing the values of the variable - prefix or environment or location in the variable values file - azurerm-secret.tfvars
# use text editor 'nano' to update the file and then press ctrl+x after you are done editing
nano azurerm-secret.tfvars