cd ~/kthw-azure-git/infra
# load variables already set for the infrastructure
source azurerm-secret.tfvars
# determine location code from location
location_code=$(az account list-locations --query "[?displayName=='$location']".{Code:name} -o tsv)
cd ~/kthw-azure-git/scripts
kubectl apply -f deployments/coredns.yaml --kubeconfig worker/configs/admin.kubeconfig
# check the newly deployed coredns pods
kubectl get pods -n kube-system --kubeconfig worker/configs/admin.kubeconfig
# output should be something like this
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
coredns-5d65dd49c8-75bzk 1/1 Running 0 5m
coredns-5d65dd49c8-n6fmb 1/1 Running 0 5m
# get cluster information
kubectl cluster-info --kubeconfig worker/configs/admin.kubeconfig
# output should be something like this
Kubernetes master is running at https://kthw-play-apiserver.australiaeast.cloudapp.azure.com:6443
CoreDNS is running at https://kthw-play-apiserver.australiaeast.cloudapp.azure.com:6443/api/v1/namespaces/kube-system/services/kube-dns:dns/proxy
To further debug and diagnose cluster problems, use 'kubectl cluster-info dump'.
cd ~/kthw-azure-git/scripts
# create a generic secret
kubectl create secret generic kubernetes-the-hard-way \
--from-literal="mykey=mydata" --kubeconfig worker/configs/admin.kubeconfig
# remote login to mastervm01
ssh usr1@$prefix-$environment-mastervm01.$location_code.cloudapp.azure.com
cd ~
# print the hexadump of the secret stored in etcd
sudo ETCDCTL_API=3 etcdctl get \
--endpoints=https://127.0.0.1:2379 \
--cacert=/etc/etcd/ca.crt \
--cert=/etc/etcd/etcd-server.crt \
--key=/etc/etcd/etcd-server.key \
/registry/secrets/default/kubernetes-the-hard-way | hexdump -C
# output should be something like this
00000000 2f 72 65 67 69 73 74 72 79 2f 73 65 63 72 65 74 |/registry/secret|
00000010 73 2f 64 65 66 61 75 6c 74 2f 6b 75 62 65 72 6e |s/default/kubern|
00000020 65 74 65 73 2d 74 68 65 2d 68 61 72 64 2d 77 61 |etes-the-hard-wa|
00000030 79 0a 6b 38 73 3a 65 6e 63 3a 61 65 73 63 62 63 |y.k8s:enc:aescbc|
00000040 3a 76 31 3a 6b 65 79 31 3a bc 6b 23 35 d8 ef 6d |:v1:key1:.k#5..m|
00000050 5c 0d 5b c2 12 5d 7b e2 a7 2b 14 9a 93 4d 9f ee |\.[..]{..+...M..|
00000060 d7 b1 fc 70 70 64 f5 de a4 b9 97 fc 30 03 0d c8 |...ppd......0...|
00000070 33 2e da 99 91 e3 df 10 27 0f 07 7a a9 68 45 9d |3.......'..z.hE.|
00000080 c6 3a 45 48 f4 6d 98 1d 50 55 4e d8 a5 ce e8 8f |.:EH.m..PUN.....|
00000090 5a 92 06 85 d0 57 e2 18 c2 33 48 af 5e c9 80 15 |Z....W...3H.^...|
000000a0 45 93 87 38 ac dd da 41 d6 56 7c 11 24 14 0c 26 |E..8...A.V|.$..&|
000000b0 94 55 f8 b6 8e 2a 11 54 29 63 b8 f2 fe 3d 19 60 |.U...*.T)c...=.`|
000000c0 c4 e0 99 76 5b 61 f4 f8 38 8c e5 74 80 c6 ef 9f |...v[a..8..t....|
000000d0 39 5f 46 41 55 a5 61 77 de 7d e5 5e 67 e2 14 96 |9_FAU.aw.}.^g...|
000000e0 84 50 10 4c 36 0f ae 95 19 bf 06 4f b8 ff b5 b6 |.P.L6......O....|
000000f0 40 fa a5 7b b6 c9 ba aa a3 59 fb 40 c2 5c cf d8 |@..{.....Y.@.\..|
00000100 dc a5 8a 31 46 5b 08 59 e1 5f 65 31 59 33 2d ce |...1F[.Y._e1Y3-.|
00000110 86 16 14 0c 05 24 fb 85 cc cf d7 c0 a2 0f 89 93 |.....$..........|
00000120 29 23 57 e9 a6 d7 62 90 89 bf 81 b4 19 61 e8 a0 |)#W...b......a..|
00000130 e3 a8 ba 34 72 8f b9 00 0f ac c1 ae ff e3 fc 4b |...4r..........K|
00000140 5b 8c 26 da 7c 7e ea 5d 29 0a |[.&.|~.]).|
0000014a
# the etcd key is prefixed with k8s:enc:aescbc:v1:key1 indicating that the aescbc provider was used to encrypt the data with the key1 encryption key.
# remote logout from mastervm01
logout
# delete the generic secret
kubectl delete secret kubernetes-the-hard-way --kubeconfig worker/configs/admin.kubeconfig
cd ~/kthw-azure-git/scripts
# create a busybox pod
kubectl run busybox --image=busybox:1.28 --kubeconfig worker/configs/admin.kubeconfig \
--command -- sleep 3600
# check the newly deployed busybox pod
kubectl get pods --kubeconfig worker/configs/admin.kubeconfig
# output should be something like this
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
busybox 1/1 Running 0 30s
# execute nslookup command in the busybox container to test dns
kubectl exec -it --kubeconfig worker/configs/admin.kubeconfig busybox -- nslookup kubernetes
# output should be something like this
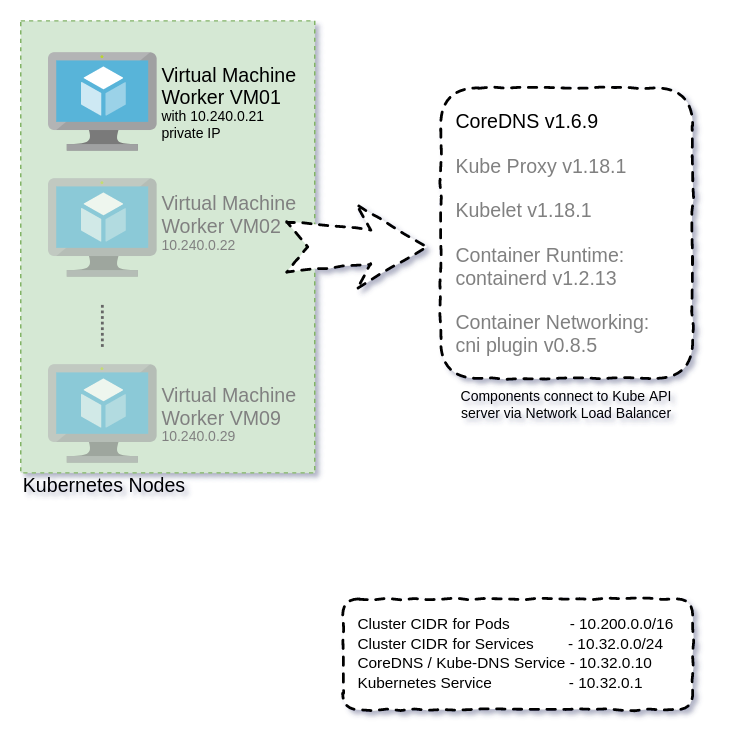
Server: 10.32.0.10
Address 1: 10.32.0.10 kube-dns.kube-system.svc.cluster.local
Name: kubernetes
Address 1: 10.32.0.1 kubernetes.default.svc.cluster.local
# delete the busybox pod
kubectl delete pod busybox --kubeconfig worker/configs/admin.kubeconfig
cd ~/kthw-azure-git/scripts
# create an nginx deployment
kubectl create deployment nginx --image=nginx --kubeconfig worker/configs/admin.kubeconfig
# collect the nginx pod name
pod_name=$(kubectl get pods -l app=nginx -o jsonpath="{.items[0].metadata.name}" \
--kubeconfig worker/configs/admin.kubeconfig)
# forward port 80 from inside nginx pod to port 8080 on host
kubectl port-forward $pod_name 8080:80 --kubeconfig worker/configs/admin.kubeconfig
# try accessing port 8080 on host in a separate terminal
curl 127.0.0.1:8080
# if you are running this on a container then execute this instead in a new command prompt / terminal
docker exec -it kthw-azure-container curl 127.0.0.1:8080
# output should be something like this
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Welcome to nginx!</title>
<style>
...
# come back to the original terminal and terminate the port forward by pressing
ctrl+c
# access the nginx pod logs
kubectl logs $pod_name --kubeconfig worker/configs/admin.kubeconfig
# output should be something like this
127.0.0.1 - - [29/Apr/2020:09:37:24 +0000] "GET / HTTP/1.1" 200 612 "-" "curl/7.68.0" "-"
# create service exposed on worker nodeport
kubectl expose deployment nginx --port 80 --type NodePort --kubeconfig worker/configs/admin.kubeconfig
# collect the service node port number
node_port=$(kubectl get svc nginx --output=jsonpath='{range .spec.ports[0]}{.nodePort}' \
--kubeconfig worker/configs/admin.kubeconfig)
# collect the workervm01 public ip address
node_ip=$(az network public-ip show -g $prefix-$environment-rg01 -n $prefix-$environment-workerpip01 --query "{IP:ipAddress}" -o tsv)
# access the node_port on workervm01
curl $node_ip:$node_port
# output should be something like this
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Welcome to nginx!</title>
<style>
...
# delete the nginx deployment and service
kubectl delete deployment nginx --kubeconfig worker/configs/admin.kubeconfig
kubectl delete service nginx --kubeconfig worker/configs/admin.kubeconfig
# create backup of the default kube config file if already exists
cp ~/.kube/config ~/.kube/config.bak
cd ~/kthw-azure-git/scripts
# export the variable with merge sequence
export KUBECONFIG=master/configs/admin.kubeconfig:~/.kube/config.bak
# write the merged kubeconfig to default kube config file
kubectl config view --flatten > ~/.kube/config
# test out the kubectl command
kubectl cluster-info
# verify if the cluster information is that of your newly provisioned kubernetes cluster
# if you wish to restore your original default kube config file
cp ~/.kube/config.bak ~/.kube/config